Nigeria
Global Piracy Up in 2018, Gulf of Guinea Leads
Piracy increased on the world’s seas in 2018, with a marked rise in attacks against ships and crews around West Africa, the International Chamber of Commerce’s International Maritime Bureau’s (IMB) latest annual piracy report reveals.Worldwide, the IMB Piracy Reporting Centre (PRC) recorded 201 incidents of maritime piracy and armed robbery in 2018, up from 180 in 2017.The Gulf of Guinea remains increasingly dangerous for seafarers. Reports of attacks in waters between the Ivory Coast and the Democratic Republic of Congo more than doubled in 2018…

Pirates Attack, Loot Container Ship
Pirates stormed a container ship off the coast of Guinea on Wednesday, making off with money and some of its cargo but leaving the crew unharmed, the government said. They fired guns and briefly held the crew hostage while they were looting the ship named Wendok, Guinea government spokesman Albert Camara said by telephone. He did not have details of the flag Wendok was flying under, the company running it, what its cargo was nor the nationalities of the crew. He said that Guinea's navy had been alerted but that the pirates had escaped before it could catch them.
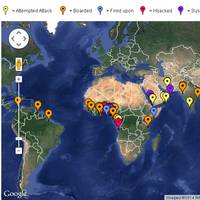
Maritime Piracy: Attacks Down, SE Asia Remains Problematic
While the issue of maritime piracy has largely fallen from the public eye, with the rapid evolution of the 24/7/365 news cycle and a never-ending list of new and globally interesting headlines, such as Ebola, there remains concerns of piracy’s effects on the broader maritime market, particularly in SE Asia. According to the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) International Maritime Bureau’s (IMB) latest piracy report, maritime pirate attacks globally are down for three years running, but there is a worrisome trend of small tanker hijacks by armed gangs escalating in Southeast Asia.

Ebola Fears Hit the Maritime Market
Brazil, Argentina and the United States have tightened port entry procedures for ships that have sailed from West Africa in a bid to control the potential spread of the deadly Ebola virus. Ebola has killed more than 3,400 people in Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia, and its spread has become a global concern -- with worries for trade, which could affect the airline and tourism industries together with seaborne activity. The virus is already threatening to disrupt logistics activity…

Piracy Offshore Africa: Securing a Continent
The late Nelson Mandela once said: “I dream of an Africa which is in peace with itself.” At the EU-Africa summit in Brussels last month, European leaders urged their African counterparts to facilitate that dream by shouldering more of the security burden in their countries, both onshore and offshore. The summit coincided with reports of renewed piracy activity in the Gulf of Aden; ongoing attacks on shipping in the Gulf of Guinea, and explosions and mass arrests in Kenya, all serving to underline the scale of that challenge.

Places of Refuge
The concept of force majeure has been broadly accepted since mariners initially encountered the perils of the sea. Persons and governments ashore have been obligated, at least by natural law, to accept and succor those in distress at sea. Concomitant with force majeure is the notion of providing a ship in distress with a place or port of refuge. A place of refuge is where a ship could go to avoid or ameliorate the peril and then depart at the earliest opportunity. While the original need for force majeure and a place of refuge was to reduce the risk to the lives of those on board the ship…
